Two major developments in the 3-D printing world, from Fictiv and (who woulda thunk it!) UPS, make me think the time has come for “distributing manufacturing” and getting away from the old massive, manufacturing mentality exemplified by Ford’s River Rouge plant.
OK, first a confession and a little history. Being short & named David, I’ve always had a fascination with David & Goliath, and you can bet who I’d root for. I also was deeply touched by two visionaries in my past:
- Steve Clay-Young, who used to run the workshop at the old Boston Architectural Center & turned me on to a neat, nearly-forgotten bit of WWII history: either Popular Science or Popular Mechanix (can’t remember which), organized a network of hobbyists with metal lathes, who played a major role in the war effort. The magazine published plans for turning metal for munitions, and these guys each worked in their workshops to make them.
- Eric Drexler, the nano-tech guru, spoke at the Eco-Tech conference in the ’90s about his vision of a bread-box-size gizmo on your kitchen counter that would churn out all sorts of customized products for you.
Now, it’s all taking place, and I suspect 3D printing will be a crucial element in the IoT-based transformation of the economy.
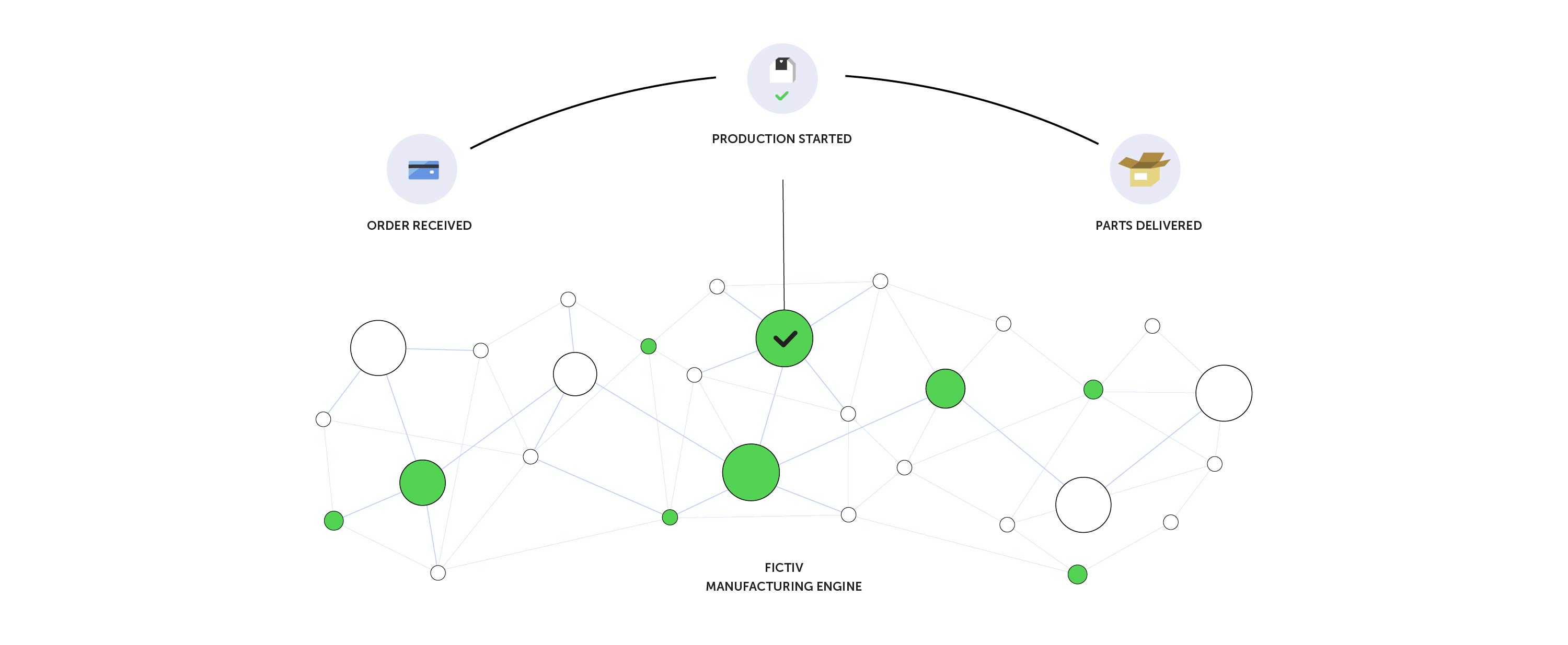
Fictiv distributed manufacturing model
Fictiv is a startup founded to “democratize manufacturing,” which just went public with its new “distributed manufacturing” service using a nationwide network of 3D high quality printers and CNC machines:
“We route parts to machine with open capacity so you don’t wait 5 days for a part that takes 5 hours…. We aggregate orders so every customer receives the benefits of large purchasing power….”
Perhaps coolest, “Parts are produced as close to customers as possible to reduce inefficiencies in logistics and shipping lead-time” so that (for an extra charge) they’re fabricated and delivered in 24 hours, and otherwise delivered in two days. I suspect that, just as having sensors on their products that results in real-time feedback allowing GE to compress the design cycle, especially upgrades, that this proximity and quick turn-around will allow designers to radically alter the design process by “failing rapidly,” just the way early spread-sheet software allowed business managers to do “what-if” hypotheticals for the first time.
By bundling orders, they give startups the bargaining power of large companies.As co-founder Dave Evans, an experienced product design pro, says, distributed, local manufacturing can even the playing field for smaller companies, especially startups just designing their first products:
“When ordering from a large manufacturing company, parts need to navigate through their complex system and then be shipped from the machine warehouse direct to the customer, increasing lead times.
From an engineer’s perspective, when you’re in the prototyping and ideation stages, time is everything and even a 1-2 day loss from a 3PL (third-party logistics player) matters significantly.
What’s important to consider here is that in manufacturing, things can and will go wrong. So when remote manufacturers inevitably have to manage errors, there’s a lot of complexity to deal with …. This is very evident in overseas mass manufacturing, which is why companies put engineers as close to the source as possible. It’s amazing how few companies consider the same principles during the early prototyping stages of a product when time is everything.
The beauty in working with smaller, local manufacturers on the other hand, is that parts can be picked up as soon as they’re ready or delivered via same-day courier, saving you the 1-2 days of shipping. In addition, if things go wrong (they always do), smaller shops have more agility, fewer organizational layers, and in general can respond more quickly compared with their larger counterparts.”

3D printing at The UPS Store
Equally important is the continuing stream of 3D services being offered by UPS. which recently announced a nationwide on-demand 3D printing network. The network will combine 3D printers at more than 60 The UPS Stores® and Fast Radius’ On Demand Production Platform™ and 3D printing factory in Louisville, KY. My friends at SAP will marry its SAP’s extended supply chain solutions will be integrated with the UPS 3D network and — most important — its global logistics network “to simplify the industrial manufacturing process from digitization, certification, order-to-manufacturing and delivery.”
If I’m correct, the UPS network will concentrate on prototyping at this point, but it’s easy to see that it could soon have a dramatic impact on the replacement parts industry. Why should the manufacturer warehouse a large supply of spare parts, just because they might be needed, when they could instead simply transmit the part’s digital file to the nearest UPS 3D printer, generate the part, and use UPS to deliver it in a fraction of the time.
Combine that with the predictive maintenance possible with feedback from sensors on products, and you truly have a revolution in product design and maintenance as well as manufacturing. It would also foster the IoT-based circular company vision that I’ve been pushing, because supply chain, manufacturing, distribution, and maintenance would all be linked in a great circle.
Sweet!