Ever so often it’s good to step back from the day-to-day minutia of current Internet of Things projects, and get some perspective on the long-term prospects and challenges.
That’s what Deloitte did last December, when it held an “Internet of Things Grand Challenge Workshop,” with a focus on the all-important “forging the path to revenue generation.”
The attendees included two of my idols: John Seely Brown and John Hagel, of Deloitte’s “Center for the Edge” (love the pun in that title!).
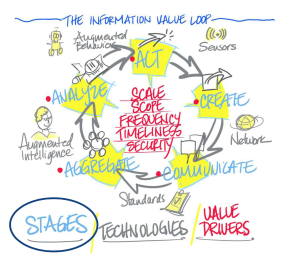
The results were recently released, and bear close examination, especially the concept of how to foster what they call the “Information Value Loop”:
“The underlying asset that the IoT creates and exploits is information, yet we lack a well- developed, practical guide to understand how information creates value and how companies can effectively capture value. The ‘Information Value Loop’ describes how information creates value, how to increase that value, and how understanding the relevant technology is central to positioning an organization to capture value. The Information Value Loop is one way to begin making sense of the changes we face. The Loop consists of three interconnected elements: stages, value drivers, and technologies. Where the stages and value drivers are general principles defining if and how information creates value under any circumstances, it is the specifics of today’s technology that connect the Loop to the challenges and opportunities created by the IoT.”
This fits nicely with one of my IoT Esssential Truths,” that we need to turn linear information flows into cyclical ones to fully capitalize on the IoT. No pussy-footin’ about this for these guys: “For information to create any value at all, it must pass through all the stages of the Loop. This is a binary outcome: should the flow of information be blocked completely at any stage, no value is created by that information.”
IMHO, this is also going to be one of the biggest challenges of the IoT for management: in the days when it was sooo difficult to gather and disseminate information, it made sense for those in the C-suite to control it, and parcel out what they felt was relevant, to whom and when they felt it was relevant. More often than not, the flow was linear and hierarchical, with one information silo in the company handing on the results to the next after they’d processed it. That didn’t allow any of the critical advantages the IoT brings, of allowing everyone who needs it to share real-time data instantly. But saying we need to change those information management practices is one thing: actually having senior management give up their gatekeeper functions is another, and shouldn’t be understated as a challenge.
So here are some of the other key points in the conference proceedings:
- In line with the multi-step strategy I outlined in Managing the Internet of Things Revolution, they concluded that incremental improvements to existing processes and products are important, but will only take you so far, at which point radical innovation will be crucial: “At first blush, the early IoT emphasis on sustaining innovation seems reasonable. Performance and cost improvement are seldom absent from the priorities of stakeholders; they are relatively easy to measure and their impact is likely more immediate than any investment that is truly disruptive. Put simply, the business case for an IoT application that focuses on operational efficiencies is relatively easy to make. Many decision makers are hard-wired to prefer the path of less resistance and, for many, truly innovative IoT applications seem too far-flung and abstract to risk pursuing. Still, organizations cannot innovate from the cost side forever.”
- Melding the public and private, “Cities have inherent societal challenges in place to serve as natural incubators of IoT solutions.” Yeah!
- As in everything else, those contrarian Millennials (who aren’t so hung up on buying stuff and often prefer to just use it) are likely to save us when it comes to the IoT: “From an innovation perspective … some of the new technologies are first marketed at the consumers. Thus, many believe that near-term innovation in IoT applications will come out of the consumer sector – spurred by the emergence of the tech-savvy Millennial consumers as a driving economic force.”
- As I’ve written before, while some customers will still prefer to buy products outright, the IoT will probably bring a shift from selling products to marketing services based on those products, creating new revenue streams and long-term relationships with customers: “As IoT makes successful forays into the world of consumer and industrial products, it may radically change the producer—buyer transactional model from one based on capital expenditure to one based on operating expenditure. Specifically, in a widely adopted IoT world, buyers may be more apt to purchase product service outcomes on some kind of “per unit” basis, rather than the product itself and in so doing, render the physical product as something more of an afterthought. The manufacturer would then gradually transform into a service provider, operating on a complete awareness of each product’s need for replenishment, repair, replacement, etc.”
Or, a hybrid model may emerge: “What may ultimately happen in a relatively connected product world is that many may accept the notion of the smartly connected product, but in a limited way. Such people will want to own the smartly connected product outright, but will also accept the idea of sharing the usage data to the limited extent that the sellers use such data in relatively benign ways, such as providing advice on more efficient usage, etc. The outcome here will also rely upon a long term total cost of ownership (TCO) perspective. With any fundamental purchasing model changes (as is taking place in owned vs. cloud resources in the network / IT world), not all suppliers will be able to reap additional economic benefit under the service model. Buyers will eventually recognize the increase in TCO and revert back to the more economical business model if the economic rents are too high.”
- It’s likely that those players in the IoT ecosystem who create value-added data interpretation will be the most valuable and profitable: “…are certain building blocks of the IoT network “more equal” than others?
“Some have argued that the holy grail of the IoT value loop resides in the data and that those in the IoT ecosystem who aggregate and transform massive amounts of raw data into commercially useful intelligence capture the real value in the IoT environment. This notion holds that commercially useful data provide insights that drive action and ultimately represent the reason that the end user pursues a smart solution in the first place. Put another way, the end customer is more apt to pay for a more comprehensive treatment of raw data than for a better sensor. Indeed, some even believe that as time passes, the gap in relative value captured by those who curate and analyze the data and the rest of the IoT ecosystem will only widen and that, on a long-term basis, players within the “non-data” part of the IoT ecosystem will need to develop some data analytics capabilities simply to differentiate themselves as something more than commodity providers. Of course, some think that the emphasis on data is overblown and argue that where the real value in the IoT ecosystem is captured depends on application. Time will tell of course. But there can be little doubt that the collection and enhancement of data is highly coveted, and analytics and the ability to make use of the vast quantities of information that is captured will serve as critical elements to virtually any IoT solution.”
I urge you to download and closely analyze the entire report. It’s one of the most thoughtful and visionary pieces of IoT theory I’ve seen (no doubt because of its roundtable origins: in keeping with the above-mentioned need for cyclical information flow for the IoT [and, IMHO, creativity in general], the more insights you can bring together on a real-time basis, the richer the outcome. Bravo!