This is a companion piece to my last post, about the HomeKit Apple unveiled last week at the WWDC — complete with the same disclaimer: Having to send huge amounts of money to Loyola of Maryland for the next three years (I feel like I’m in the Weimar Republic and must carry tons of money to Baltimore in a wheelbarrow, LOL) to secure my youngest’s sheepskin has led to a part-time sales job at the Apple Store — which doesn’t give me any inside insights into their strategy. Rest assured that nothing that will ever appear in this blog about Apple will be gathered from anything other than public sources. I know only what you know, and the opinions expressed here are solely my own.
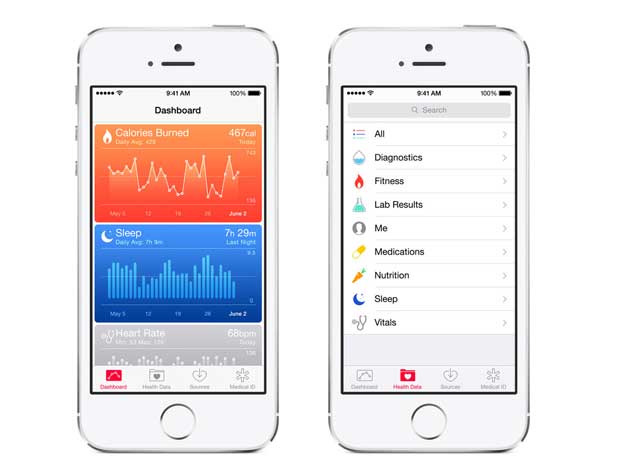 The other IoT developers’ kit that Apple unveiled was the HealthKit, combined with a new Health app that will be released along with iOS8.
The other IoT developers’ kit that Apple unveiled was the HealthKit, combined with a new Health app that will be released along with iOS8.
They say the app will “give you an easy-to-read dashboard of your health and fitness data.”
The developers kit is designed to help health and fitness apps (… and wearables) work together.
Apple teases us that the package “just might be the beginning of a health revolution.”
Could it be the key to finally expanding interest in personal health data beyond those of us who are proud members of the Quantified Self, and could it be the catalyst in the revolution that I’ve predicted before: a new healthcare paradigm in which patients, empowered with data about their daily health stats, might become real partners with their doctors, improving their health while reducing the need for costly hospitalizations?
We’ll see, but I’ll be watching carefully, because — speaking of paradigm shifts — I wonder if the HealthKit and HomeKit, combined, may provide the tools (oops, originally typed fools.. LOL) to make my vision of empowered seniors, “aging in place” a reality.
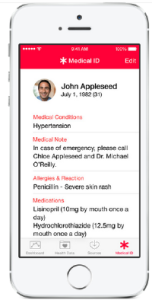
Emergency Card
One feature of the Health app really resonated with me, because it offers an up-dated version of two sadly-dated “21st-Century Disaster Tips You WON’T Hear From Officials” videos that I did waaay back in 2007: one suggesting that you put your electronic health record on one of those new-fangled (LOL) thumb drives, and another, that you put an ICE (In Case of Emergency) listing on your cell-phone (pre-smartphone) directory. The Health App would combine that information on an “Emergency Card” that would be accessible to EMTs even from your lock screen. Neat!
Dr. Joe Kvedar, director of the Partners Health Care Center for Connected Health, my go-to guy for m-health analysis, struck a cautionary note:
“‘Expecting people to have an ‘aha’ moment because you’ve created a place where they can store data—you’ll be disappointed ….It needs to be much more compelling.’”
Apple seems to get it that privacy and security, always critical with any IoT device or app, would be of paramount importance when it comes to sharing one’s personal medical data:
“Patients could choose to share blood pressure readings with their doctor but not with another app, for example. Even so, patients are sure to be particularly sensitive about who has access to such information.
“’I think that the people doing these integration platforms need to have a privacy mechanism that is believable,’ says George Westerman, a research scientist at the MIT Center for Digital Business. ‘That takes not only a good policy but a brand people trust.’”
The prestigious Mayo Clinic is on-board, updating its app to coincide with release of Health, according to MIT’s Technology Review:
“The clinic’s app is expected to offer additional services, including ways to monitor patients with asthma or diabetes. ‘If you see the glucose levels rising … you could interact with [the patient] if they had a question, intervene appropriately, and then decrease the need for an emergency room visit or a hospital admission, which we know drives up hospital and patient costs,’ says John Ward, Mayo’s medical director for public affairs.”
Truth to tell, I don’t always record my diet, weight and exercise exercise every day with Lose It!, and I’m well aware that most people who try QS apps don’t keep at them. However, I suspect the HealthKit, because of the mindshare and platform that it will create, may mean this will succeed where Google Health and Microsoft’s HealthVault have failed, and that it will eventually be cool to know what your health stats are — and to improve them.